Spanish and English come from the same Indo-Uranian language family. But these two languages come from different sub-branches. English belongs to the Germanic branch while Spanish belongs to the Italian branch. Therefore, if you study the language, you will notice the difference between Spanish and English. Spanish is older than English, and their distinct development was influenced by other languages through conquests and other forms of contact with other cultures.
Spanish is the second most spoken language in the world after Chinese while English is third. However, English is the official language in 27 non-sovereign and 55 sovereign countries worldwide. On the other hand, Spanish is the official language in 20 countries. Both languages are official languages of the United Nations.
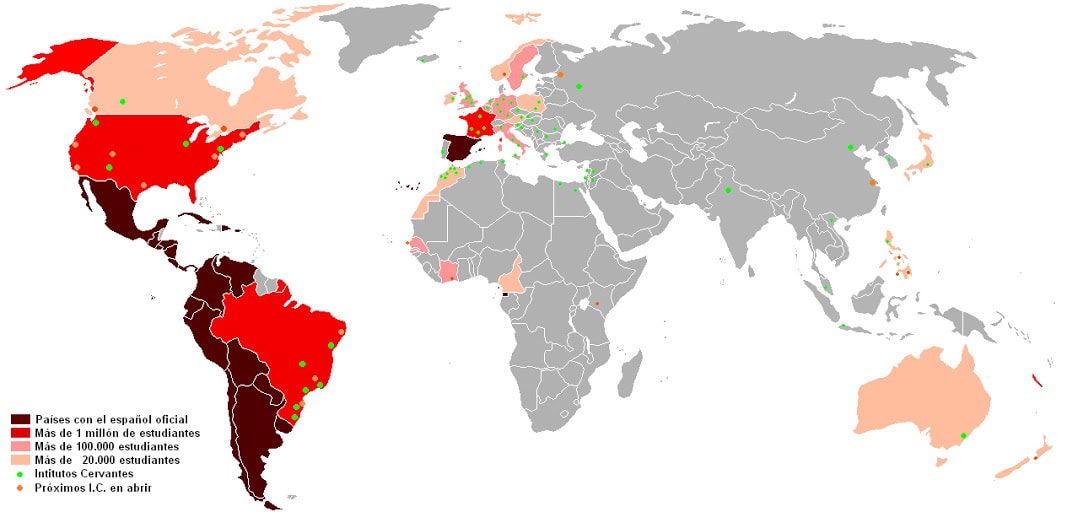
Like English, you can communicate with many people around the world who speak Spanish as a first or second language. If you are looking for a second language to learn, know that Spanish is one of the most studied languages in the world. But like most languages, the difficulty or ease of learning a language depends on the student and the primary language he or she speaks. English speakers may find it difficult to learn Spanish. On the other hand, Romanian speakers will have an easier time learning Spanish because Spanish is related to other Romance languages, such as Italian, French, Romanian, and Portuguese. .
Note: Difference Between Language Localization and Translation
Main differences between Spanish and English
What you have read so far are the features that distinguish English from Spanish. All languages have different characteristics, making each language unique. Most of the major differences between English and Spanish are found in sentence construction and grammar.
There may be some overlap but the Spanish language has a different structure and development history unlike English. Some differences are also found in the rules, pronunciation and spelling of Spanish.
Here are 10 key differences between English and Spanish
1. Sentences and questions in Spanish can be written the same way.
In English, it's easy to distinguish between a question and a clause. The verb in an English question comes first. If it is a clause, the subject is placed before the verb. In Spanish, sentences are written in a similar way, for example, “Juan is talking with the man” or “Juan está hablando con el hombre.” You write it the same way when asking a question, with adding a reverse question mark before the clause and a question mark at the end of the question.
Note: Key Differences Between English And Arabic
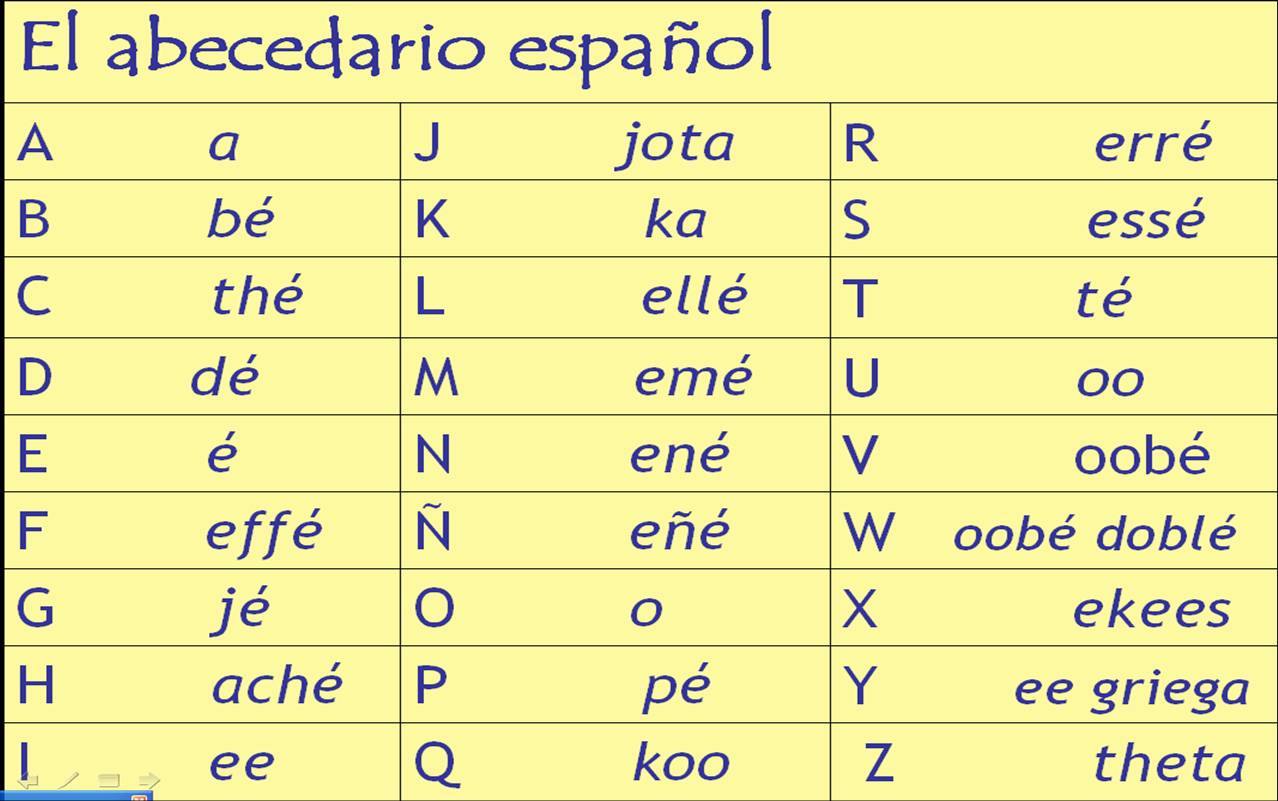
2. Spanish has more letters
Spanish has 27 letters of the alphabet including /ñ/ while English has only 26. However, Spanish has more sounds. Spanish also has /ch/, /ll/, /rr/ and accented vowels /á/, /é/, /í/, /ó/, /ú/ and letters (vowels and consonant) with an umlaut, two dots on top of a letter, such as /ü/. It is a sign indicating how to pronounce that letter.
3. W is a foreign letter
Do you believe that the letter W, included in the Spanish alphabet is considered a foreign letter? That is only used for borrowed words. You can try searching for Spanish words that start with w to see that clearly.
4. All Spanish verbs end in only three letter phrases
English verbs often have many forms. In Spanish, all verbs end in –ar, -er or –ir.
5. Order of words and adjectives
In English, it is common to have an adjective before a noun, because the purpose of an adjective is to modify or describe the noun. In Spanish, adjectives are placed after nouns. It may take some adjustment for Spanish learners to remember this if the student is an English speaker. However, if the adjective is countable, it should be placed before the noun. For example, “the only house” should be written as “la única casa” (instead of la casa única).
Note: Difference Between German And English
6. The Spanish verb 'to be' has two forms
Spanish has two forms for the verb 'to be'. One is ser and the other is estar. Ser vs estar is used in different way. When you talk about permanent or permanent properties, you use ser. Verbs are used for descriptions, such as name, religion, nationality, and physical description. You use the verb when describing an occupation (to earn a living) or the work of a person for a period of time, such as being a student or a gardener. Ser is used to describe someone's personality or time, year, day, month and day.
Ser also applies when describing someone's or something's background, as well as relationships, whether it's romantic, friendly or familial.
Estar is a verb used to refer to temporary places and states. Estar is also used to describe emotions, conditions, actions, places, and positions.
Position can be a posture or physical position of a person or where something is placed. You can use estar to indicate the permanent location of a room, or the temporary location of something.
The exception is for parties or events. In this case, ser is used instead of estar.
Estar is also used for ongoing actions, which are followed by a present participle or a past participle.
Note: For Spaniards, death is an action in progress, so estar is used when talking about death. Mental and physical conditions that can change within hours or days are described by estar. The same is true of emotions that can change quickly.
Note: Difference Between English And Russian
7. Nouns in Spanish have gender
Some nouns you know are feminine, considered masculine in Spanish. As a general rule, nouns ending in o, accented vowels, e, -ma, and nouns ending in a consonant minus d and z are masculine. It should be noted that some nouns ending in the letters mentioned above are feminine.
Examples of masculine nouns:
- postman
- niño
- tio
- ,
- fragrance
- bookcase
- humming-bird
- aji
- cushion
- rumor
- SCHEDULE
- language
- drama
Exceptions (these are feminine nouns):
- hand
- photo
- radio
- key
- street
- snow
- blood
- mother
- miel
- shawl
- flower
On the other hand, most nouns ending in /a/ are feminine, such as:
- nurse
- daughter
- guitar
- pink
- Swimmingpool
Similarly, other nouns ending in the consonants /d/ and /z/, as follows are also feminine.
- health
- happiness
- vertud
- peace
- light
- irritation
- song
The following words are some exceptions, as they are considered masculine:
- enigma
- map
- planet
- day
- work
- problem
- climate
- panda
- abbot
- avalanche
- rice
- fish
- corn
- pencil
- ansion
- notice
- rocion
- sentencion
Before masculine nouns are articles el (singular) and los (plural). Before feminine nouns are articles "la" (singular) and "las" (plural).
Notes on adjectives and prepositions
The articles and adjectives you use must match the descriptive nouns in terms of gender and number. For example, apple is female, so you should say “La manzana es roja” or “The apple is red.” But bananas are masculine, so it should be “El platano es amarillo” or “The banana is yellow.”
Here is another example:
Female form:
- The red flower – la flor roja
- The red flowers – las flores rojas
In the first sentence, everything is singular – articles, nouns and adjectives. Things change in sentence b when the flower is in the plural.
Male form:
- The red cat – El gato rojo (singular, male)
- The red cats – Los gatos rojos (plural, masculine)
8. Spanish has simpler negatives
English has different prefixes you can use for negatives, and the rule says you shouldn't use two negatives. It should be a mix of affirmation and negation. In Spanish, the rules of grammar say that two negatives should be used. For example, when you say, "I don't want anything" in English, Spanish is equivalent to "No quiero nada." The direct translation of the sentence “I do not want nothing” shows how “no” and “nada” work together, making it easier to build negative sentences in Spanish.
9. Subjects are sometimes omitted in Spanish
The different conjugations of Spanish verbs can be difficult to memorize. However, once you understand how to apply each conjugation form, you can omit the subject when speaking.
Note: Difference Between Chinese And English
10. The verb 'tener' can be used to express someone's feeling
Tener means 'yes.' Often this verb is used to express your age, something attributed to you, or what you are feeling right now. So when you hear a Spanish speaker say, “Tengo 20 años” (I have 20 years), that person is saying that he or she is 20 years old. If you are hungry, you say “tengo hambre”, or “tengo miedo” if you are scared.
Professional Spanish and English Translation Services
There are many differences between Spanish and English and the above are just some of the highlights that you will encounter if you are learning Spanish. Whenever you need to communicate or have a written document in Spanish that you would like to understand better in your language, contact Idichthuat. We are a professional translation company with high expertise in Spanish translation service and English. Our translators are domestic and foreign experts who will satisfy all the needs of our clients.
Contact us today for the fastest service quote and consultation.
| ✔️ See more related information: | 👉 Reliable, Cheap, Professional Swedish Translation Chuyên |
| 👉 The Most Professional Electronic Translation | |
| 👉 Quick Translation of Seafood Documents | |

Nguyen Trung Khang - Talented interpreter and translator, passionate about translation
Nguyen Trung Khang is a talented interpreter and translator, with many years of experience in the field of translation and linguistics. He graduated from Ho Chi Minh City University of Education, majoring in Linguistics in 2015.
After graduating, Mr. Khang participated in a professional interpretation and interpretation training course at the University of Foreign Languages - Hanoi National University. He achieved a high-level certificate in interpreting and interpreting, and was also awarded a master's degree in linguistics.


