China is the largest country in Asia, covering a total area of 9.596.961 square kilometers or 3.705.407 square miles, and is unique in its many different characteristics, including the diversity of languages spoken. in China. At the beginning of 2019, China's population was estimated at 1,4 billion people, accounting for 18,41% of the world's population, according to United Nations estimates.
Number of Languages Spoken in China
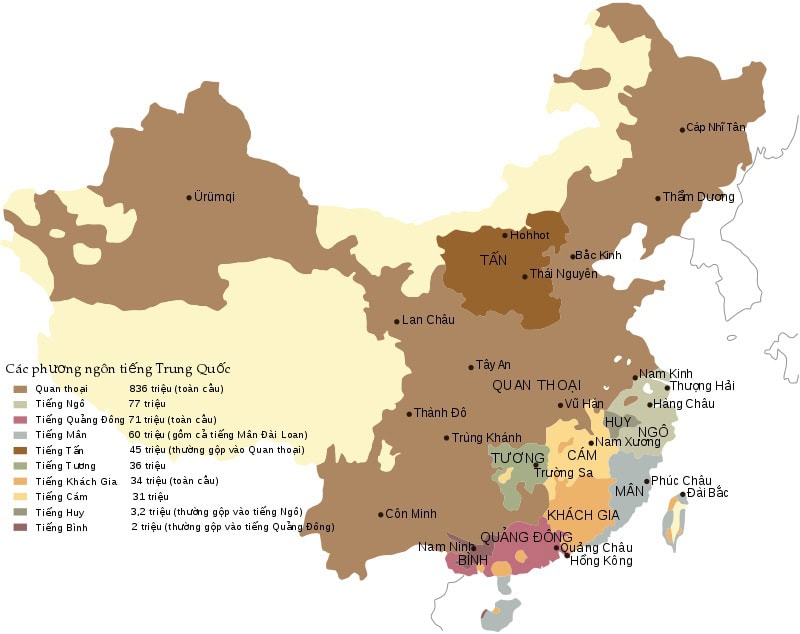
China also stands out in terms of the number of languages spoken in the country. According to the latest data from Ethnologue, China has 302 separate living languages, of which 276 are indigenous. The United Nations celebrates April 20 as Chinese Language Day, as part of an organization that strives to promote the six official languages and celebrate linguistic and cultural diversity.
Incidentally, April 20 is also the Chinese celebration of Guyu (Raindrops/Rain of Millet) which honors Cang Jie. It's an imaginary figure in Chinese folklore, said to have invented Chinese characters. According to folk tales, ghosts and gods cried and millet seeds fell from the sky when the characters were invented by Cang Jie. In China, they classify their language as dialect, for political reasons. Linguists may disagree, so in this article the use of language and dialect will be interchangeable.
The Chinese language belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is one of the largest language families in the world. Chinese is spoken by 1,3 billion people around the world. Chinese, perhaps the most recognized form of the Chinese language, is just one dialect. The language is widely spoken, but Chinese speakers will not be able to understand Cantonese, another Chinese language variant. There are many differences between Chinese dialects. Despite the number of dialects, Standard Chinese or Mandarin has been the official language of the country since the 1930s.
Note: Difference Between Chinese And English
Official Chinese Directive Thị
While China's national policy allows for cultural and regional autonomy and each region and dialect group is allowed to use their own language, they are also required to understand and speak the national language, it is Chinese or Standard Chinese as the lingua franca.
Prior to the 20th century, the various Chinese governments were not overly concerned with the language issue. But in 1949, the government strongly supported the idea of having only one official language, although concrete actions were taken only in 1955. That year Chinese was chosen as the national language and an indicator. The directive was enacted to teach this language in all schools and should be used in all aspects of life, from the military to the press, commerce, industry, broadcasting as well as the public sector. interpretation and translation. This reform included changes to Chinese writing, with the government abolishing some characters and ordering the simplification of hundreds of characters.
Chinese Language And Some Popular Dialects
According to linguists, there are seven (or 10) main groups in the Chinese language. Chinese is the largest and the other groups also have several sub-dialects. Within each group, some dialects are mutually intelligible while others are not. One of the reasons for this is that many areas are geographically isolated. Without contact and interaction with the nearest neighbors, they only understand the dialects spoken in their area. It is also important to note that these groups also have millions of speakers.
It is difficult to fully grasp the complexity and variety of the Chinese languages. Dialect speakers may not understand each other, due to the accent and pronunciation of the characters. While the languages spoken in China are numerous, in about 7 major groups.
Note: Difference Between Traditional and Simplified Chinese
High School
Mandarin is the leading language among the group, also known as North Chinese, spoken by about two-thirds of China's population. Other names for Mandarin include Standard Chinese, Beijing, Hong Kong, and Standard Chinese. In China alone, Mandarin is spoken as a first and second language by 1,082 billion people. Worldwide, the total number of Mandarin speakers is 1,116 billion.
There are four subdivisions of Mandarin Chinese.
- North Chinese is spoken in Northeastern provinces such as Manchuria, northern China, and in the Capital, Beijing.
- Northwestern Central is spoken in Baoji and the northwestern provinces of Ningxia, Xinjiang, Qinghai, Shaanxi and Gansu.
- Southwest Central is spoken in many regions of southwestern China, Sichuan, Yunnan, Guizhou and Chongqing.
- Nanzhong is spoken in the provinces of Nanjing, Cantonese and Hainan.
Tones in Chinese show different meanings. Mandarin has four tones such as level, up, up, and down. These tones distinguish syllables and words use the same vowels and consonants to define the word's meaning. Chinese consists of only a few words ending in a consonant, monosyllabic words and word elements but no markers to indicate parts in speed or inflection.
Corn
On the coastal area in Shanghai, Wu is the dialect spoken in China. Corn is also known as Dong Jin and Changzhou. In 2017, there were 81,4 million people speaking Wu in China. Worldwide, the total number of Wu speakers is 81,5 million. This language is spoken in several different provinces such as Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Fujian, Anhui and the municipality of Shanghai. Maize is the second most common variant of the Chinese language.
The Wu language spread from the 5th century cultural center called Suzhou. This language gained more importance during the Ming Dynasty, because Shanghai was an important metro area at the time. Wu has preserved the original pronunciation stops and uses about seven or eight sounds to distinguish the meanings of words and word components that use the same vowels and consonants.
Note: Compare The Similarities And Differences Between Chinese And Japanese
Ton
Jin is a dialect that is not easily understood with other Chinese dialects. It is also known as Cantonese. This language ranks second after Mandarin in terms of usage. There are about 62 million people speaking Jin in China but it is spoken by 73,5 million Chinese worldwide. Jin or Cantonese is mainly spoken in Guangdong, Hunan and Hainan provinces and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Cantonese has 10 sub-dialects with Cantonese as the standard.
Besides China, Cantonese is spoken in Australia, Brunei, Canada, Hong Kong, Macao, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Suriname, Thailand and Vietnam.
Cantonese still has many features of ancient Chinese, including the use of ending consonants. It has six syllables and while there are fewer initial consonants, it has some markedly different syllables. Most Chinese immigrants before the mid-20th century spoke Cantonese or Jin.
Similarity
In Southern China, Hunan Province, the predominant dialect is Xiang. Because most of the provinces are surrounded by Mandarin-speaking territories, the latter has a major impact on the Xiang language. Among the languages in the major groups, Xiang is the most similar to Mandarin. This language is divided into New Future and Old Xiang. New variants are spoken in Hunan, Changsha. Old dialects prevail in Song Phong and many areas in Hunan. The Old Xiang is similar to the Wu language in some respects. This dialect uses five sounds and has many different initial consonants than the other major Chinese dialects.
Man
The population of Fujian province mainly speaks Min. Min is also spoken in many parts of Taiwan, Hainan, Zhejiang and Guangdong.
The rosary is divided into five main variations:
- Minnan has about 50,5 million speakers in Taiwan and Southeast China, also with several dialects, including Amoy or Xiamen. Amoy interpreters use dialects for transactions.
- Mindong has 10,3 million speakers.
- Minbei has 11 million speakers in several regions of the world, including Singapore, as of 2017.
- Phu Tien, is spoken by about 2,6 million people in the Tien Du and Putian districts of Fujian province and is also spoken in Singapore and Malaysia.
- Minzhong is spoken in the cities of Yong'an and Sanming and Sha district in Fujian province. There were about 3,5 million speakers of the language in 2017.
Man is a combination of grammar and vocabulary from many periods in the history of the Chinese language.
Although there are many people who speak Min, its development history makes it difficult to find Chinese characters that match the dialect, as most characters are made for Mandarin Chinese. Therefore, Min script uses some Roman characters in place of the unavailable Mandarin Chinese characters.
Min speakers also use a special pronunciation called Tibetan Min that retains the final consonants used in ancient Chinese for literary purposes.
Cam
More than 22 million people, most of them living in the provinces of Hunan, Fujian, Jiangxi and Hubei speak the Cam language, also known as Jiangxi. The Cam language shares some similarities with Hakka and its dialect. Cam retains many archaic words that are no longer used in Mandarin and are partially understandable to Wu and Mandarin speakers, but more understandable to Hakka speakers.
Note: 05 Reasons To Choose Chinese Localization Service
Guest House
Hakka differs from the other groups on this list because it is spoken mainly in isolated areas, despite its wide distribution. Due to the isolation of the speakers, it has about 13 different dialects.
Hakka has 43,5 million speakers in China and an estimated total of 48,5 million speakers including other fields. Hakka are heavily concentrated in the northeast and east of Guangdong province, especially in southern Jiangxi, Hunan, Hainan, Guangxi and Fujian as well as the western and southwestern areas of the provinces. Sichuan province. Hakka speakers can be found in Brunei, Cambodia, Hong Kong, Taiwan, French Guiana, French Polynesia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Panama, Suriname, Singapore and Thailand. Most immigrants in Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand speak Hakka. This language has six sounds like Cantonese and shares similarities with Cam and languages like Hakka borrowed heavily from Cantonese.
These are the seven main groups of different Chinese languages. Each group has several dialects, making the Chinese language very complex. Many of these are specific to individual localities, requiring deep cultural and geographical knowledge from translators and interpreters. In mainland China and many overseas regions, Simplified Chinese is the official script used in China, applied to all texts. However, there are places like Singapore that have developed their own style and vocabulary. With variations, you should only work with a professional translator to ensure that your Chinese translation is correct.
10 Diverse and Widely Used Languages in China
Mandarin
Mandarin is known as the “common language” and has been the official language of China since 1913. The language is based on the Han ethnic group, originating in the North, and based on the variant of Mandarin used. during the Manchu Dynasty in Beijing.
Standard Mandarin is often referred to as "Chinese" in China, but the term pǔtōnghua (meaning "common language") is commonly used in China. Mandarin is such an important language that it has been included in the list of one of the six official languages of the United Nations.
uyghur
The language of about 11 million people in China, the Uyghur language is primarily the language of the Uyghur community located in much of the western part of China.
The language is derived from Turkish and influenced by Persian and Arabic, but although it is spoken by people in China, it belongs to a completely different language group from English. Mandarin, written Arabic script.
Chinese
When answering the question of how many languages are in China, Mandarin and Cantonese dominate. In fact, the two most widely known and spoken variants of Chinese are Mandarin and Cantonese. For those who don't know the difference, these two languages seem to be interchangeable.
The word “Cantonese” has an interesting history. Guangzhou – the capital of China's Guangdong province was formerly known as Guangdong, from which the name "Cantonese" was derived. There are about 60 million Cantonese speakers in China, mainly in Guangdong province and Hong Kong, where Cantonese is the primary language.
hmong
The Hmong language, also known as Chuanqiandian Miao, is the language of about 3 million people in China, most of which reside in the provinces of Sichuan, Yunnan, Guangxi and Guizhou. This language is part of the Hmong-Mein family, spoken in the mountainous regions of southern China and Southeast Asia.
Kalmuck
Mongolian is of Mongolian origin but is most widely spoken in China's Inner Mongolia province. Mongolian is part of a separate language group known as Mongolian and is spoken in the provinces of Liaoning, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Gansu and Xinjiang. This language had such an influence on China that one of China's main dynasties was Mongol.
Chinese Hakka
Spoken by the Hakka people, it is the language of 30 million people, making it one of the main regional languages of China. However, due to the fact that the speakers of this language live scattered throughout China, Hakka has developed many distinct dialects.
Korean
When one classifies the most widely spoken languages in the world, this language is considered as one of them, taking 17th place. While most Korean speakers reside in the North and South Korea, a small number of them live in the northeastern province of Jilin. Korean is also one of the two official languages of the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Province, northeast of Jilin.
Shanghai
Many varieties of Wu are spoken by native Shanghainese, Shanghainese has a very small 29% lexical similarity with Mandarin and is therefore used to distinguish between Chinese natives and immigrants because of a A significant portion of Shanghai's population are migrant workers.
Kazakh
Kazakh – a minority language in China, belongs to the same Turkic family as Uyghur. Only 27% of China's Kazakh population speaks, it is concentrated mainly in the Kazakh Autonomous Province.
Tibet
Tibetan is a sub-language of China and is divided into three main groups: Tibetan, Kham and Amdo. It is not surprising that Tibetans speak Tibetan and Standard Tibetan is often referred to as Lhasa Tibetan because it is based on Lhasa's speech.
Looking at the information above about the number of languages in China, it is not surprising that it is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse countries in the world.
A professional translation company like Idichthuat understand language diversity. With a country as large as China, there are many dialects that need to be understood. Our translators fully understand the difference between different Chinese dialects. All of our translators are experienced professionals in various fields of Chinese translation. Please contact Idichthuat today to experience Chinese translation service quality - accuracy - fastest and after-sales with every customer!
Blog Sharing Translation Experiences

Nguyen Trung Khang - Talented interpreter and translator, passionate about translation
Nguyen Trung Khang is a talented interpreter and translator, with many years of experience in the field of translation and linguistics. He graduated from Ho Chi Minh City University of Education, majoring in Linguistics in 2015.
After graduating, Mr. Khang participated in a professional interpretation and interpretation training course at the University of Foreign Languages - Hanoi National University. He achieved a high-level certificate in interpreting and interpreting, and was also awarded a master's degree in linguistics.